Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Binocular Vision Dysfunction (BVD) are two distinct conditions that can present similar symptoms. However, it’s important to understand that they are different disorders that require different types of treatment. According to Studies, about 50% of the individuals diagnosed with ADHD may have a vision deficit that can affect their ability to learn and reading comprehension. This can be due to an undiagnosed misalignment of the eyes (BVD). In this article, we will define and explain both conditions, discuss their causes, signs and symptoms, differences, and treatments.
Understanding ADHD
ADHD is a chronic neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by a persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactivity-impulsivity that interferes with daily functioning.
The exact cause of ADHD is unknown, but research suggests that it may be due to a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurobiological factors. Some studies have found that individuals with ADHD have lower levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, which can affect attention and impulse control. Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) is a subtype of ADHD that typically does not involve hyperactivity or excessive movement.
Signs and symptoms of ADHD
The symptoms of ADHD can be categorized into three types: inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity.
Inattention symptoms include difficulty paying attention to details, being easily distracted, forgetfulness, and difficulty organizing tasks.
Hyperactivity symptoms include fidgeting, restlessness, excessive talking, and difficulty staying seated.
Impulsivity symptoms include interrupting others, difficulty waiting for one’s turn, and acting without thinking.
Understand Binocular Vision Dysfunction (BVD)
Binocular Vision Dysfunction (BVD) is a condition that affects the way the eyes work together. BVD occurs when the eyes have a vertical or horizontal misalignment and cannot work together in a synchronized, healthy manner to create a single image. BVD can occur as a result of an abnormal visual system caused by a stroke, refractive error, brain injury, concussion, or other neurological disorders. To compensate for the misalignment, the eye muscles around your eyeball overwork in an attempt to synchronize the two eyes together, but this can cause a range of symptoms.
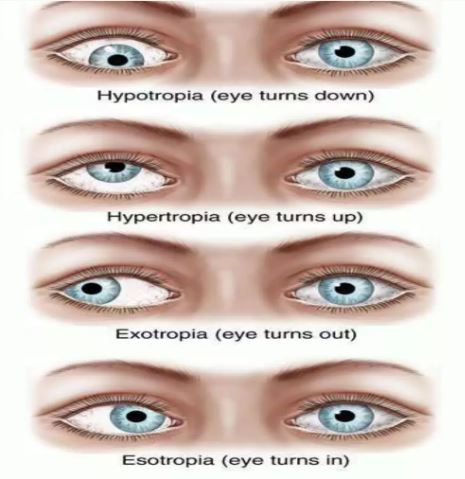
Signs and symptoms of BVD
- Headaches or Migraines
- Eye strain
- Double vision
- Nausea or motion sickness
- Difficulty reading
- Blurry vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Skipping Lines When Reading
- Words “swimming” around on the page when reading
- Difficulty maintaining focus
- Tilting of the head to see.
- Anxiety in large spaces that have high ceilings
Differences between ADHD and BVD
The symptoms of ADHD and BVD can overlap, which can make it difficult to differentiate between the two conditions. However, there are some key differences in the signs and symptoms associated with each disorder.
| Feature | ADHD | BVD |
| Nature of the Condition | Neurodevelopmental disorder, is primarily a cognitive and behavioral disorder. | Vision-related problem, when both eyes are unable to work together as a team |
| Symptoms | symptoms tend to be more consistent | BVD symptoms can be intermittent |
| Underlying Causes | Genetic, environmental, neurological | Abnormal visual system caused by a stroke, refractive error, brain injury, concussion, or other neurological disorders |
| Diagnostic Process | Behavioral observations, interviews | Eye examinations, specialized vision testing |
| Treatment Approaches | Behavioral therapy, medication (if needed) | Prescription glasses, vision therapy, interventions |
| Prognosis | Lifelong condition with manageable symptoms | Improvement and potential resolution with treatment |
Why BVD Gets Mistaken for ADHD
BVD can often be mistaken for ADHD because many of the symptoms and the manner of their actions are similar. Additionally, the underlying cause of BVD is not always easy to diagnose, which can lead to a misdiagnosis of ADHD. Vision difficulties can affect concentration and ability to complete tasks, symptoms of ADHD.
When a child or adult presents with symptoms of ADHD, it is important to rule out any underlying visual conditions, such as BVD, before making a diagnosis. A comprehensive eye exam can help identify any visual problems that may be contributing to the symptoms. Lack of the appropriate tests can easily lead to misdiagnosis.
Treatments for ADHD and BVD
The treatment for ADHD typically involves a combination of medication and behavioral therapy. Medications such as stimulants and non-stimulants can help improve attention and reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and parent training, can help individuals learn coping strategies and improve social skills.
The treatment for BVD typically involves prescription lenses or prisms that can help align the eyes and improve visual function. Vision therapy, which involves a series of eye exercises and activities designed to improve visual skills, can also be helpful in treating BVD.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while ADHD and BVD share some similar symptoms, they are two distinct conditions that require different types of treatment. It is important to understand the differences between the two conditions and to seek a comprehensive evaluation from a qualified healthcare provider to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.